How to Generate a Semantic Model in Precog
Precog can automatically generate semantic models for your data sources, enabling natural language queries through Snowflake Cortex Analyst. This guide walks you through enabling semantic modeling and generating your first model.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- You have a Snowflake destination configured in your workspace
- You have at least one data source connected
Steps
1. Open Your Workspace
From the Organization Dashboard, select the workspace containing the source you want to model.
2. Enable Semantic Modeling
You can enable semantic modeling either when creating a new source or by updating an existing source.
Option A: When Creating a New Source
During source setup, you'll see the Source Use Cases section. Select the option to enable semantic modeling before completing the source configuration.
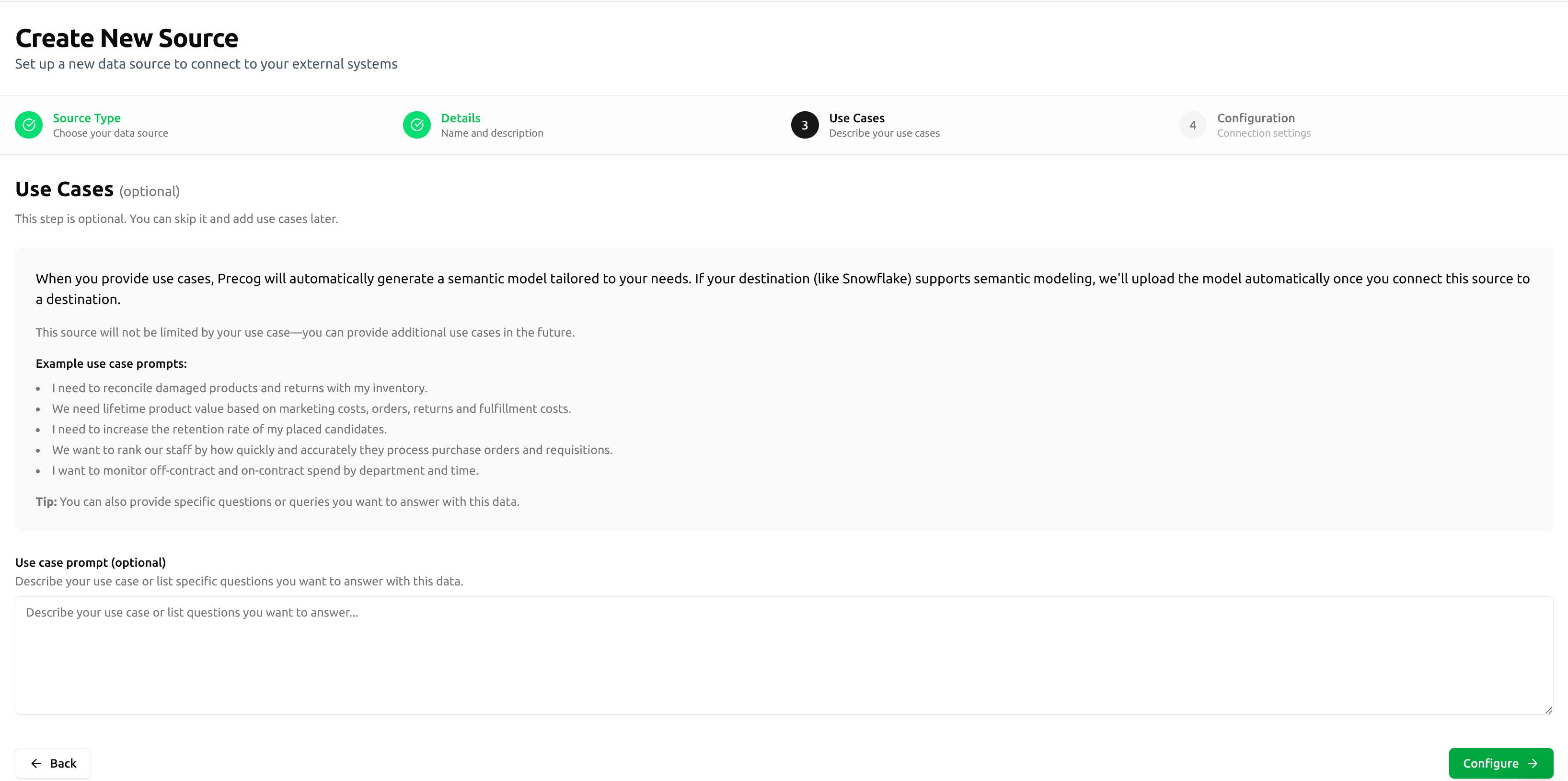
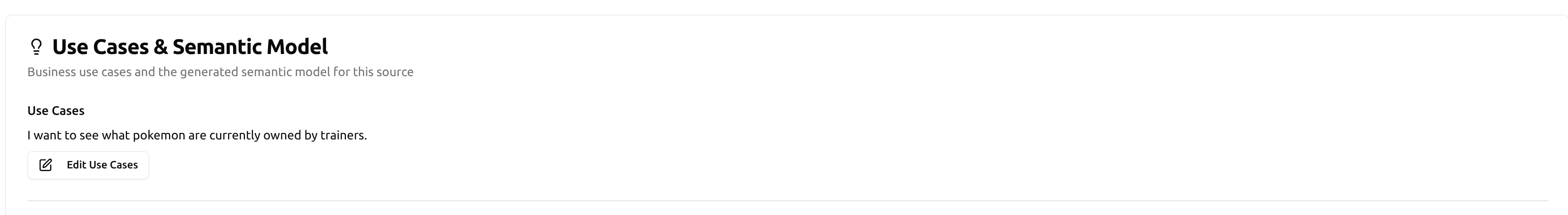
Option B: For an Existing Source
- In the workspace menu (left-side navigation), select Sources
- Select the source you want to generate a semantic model for
- On the source details page, locate the Source Use Cases section and select Edit
- Enable semantic modeling and save your changes
3. Run a Data Load
Once semantic modeling is enabled, you need to run a data load to generate the model.
For a new source: Create a connection that includes this source and your Snowflake destination, then select Run Now.
For an existing source: Go to Connections, find a connection that uses this source, and select Run Now to trigger a dataset reload.
During this run, Precog will:
- Load your data into Snowflake
- Analyze your source schema
- Generate a semantic model YAML file
- Upload the model to Snowflake
4. View Your Semantic Model in Snowflake
After the run completes (typically within 5 minutes), your semantic model will be available in Snowflake. You can:
- View the YAML file directly in Snowflake
- Edit the model to add descriptions, synonyms, or custom metrics
- Use the model with Snowflake Cortex Analyst for natural language queries
Result
Your semantic model is now generated and available in Snowflake. Each time you run the connection, the model updates to reflect any schema changes in your source.
Users with access to your Snowflake warehouse can now use Cortex Analyst to ask natural language questions about your data, such as:
- "What were total sales last month?"
- "Show me the top 10 customers by order value"
- "How does this quarter compare to last quarter?"
Why Semantic Models Matter
Self-service analytics: Business users can query data without writing SQL or waiting for analyst support.
Consistent definitions: Metrics like "revenue" or "active customer" are defined once and used consistently across queries.
Faster insights: Natural language removes the translation step between business questions and data queries.
Practical Advice
Write clear use cases: The quality of your semantic model depends on how well you describe your use case. Include specific metrics, entities, and the types of questions you want to answer. See Writing Effective Use Case Descriptions for examples and templates.
Start with one source: Generate semantic models for your most important data source first. Expand to additional sources once you're comfortable with the workflow.
Review the generated model: While Precog creates a solid baseline, you may want to add business-specific descriptions or synonyms to improve natural language matching.
Keep sources focused: Semantic modeling currently works for one source at a time. If you need cross-source analytics, consider which source contains your most critical business data.
Next Steps
Once your semantic model is generated, you can improve its accuracy over time:
- Maintain and Optimize — Learn how to add verified queries and use Snowflake's suggestions to make your model smarter
- Semantic Modeling FAQ — Common questions about viewing, editing, and troubleshooting your semantic model
- Semantic Modeling Explained — Deep dive into how semantic models work and best practices for use case descriptions